Cloud Computing has been advantageous over the past two decades, and despite the data pointing to the business efficiencies, cost-benefits, and competitive benefits, a large portion of the business community continues to operate without it. Cloud Computing is one of the leading technologies driving how we work and play. In addition to helping companies reduce IT headaches, the cloud also helps boost productivity and security. It also helps small businesses leverage the latest computing technology for a much lower cost. According to a study, 69% of companies already use cloud technology in one capacity or another, and 18% say they plan to use Cloud Transformation at some point. As this data shows, an increasing number of tech-savvy businesses and industry leaders recognize the many benefits of Cloud Computing Services, but more than that, the Cloud Platform is used to run their organizations more efficiently, better serve their customers, and dramatically increase their overall profit margins.
Cloud Computing is the use of hosted services, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software over the internet. The data is being stored on physical servers, which a cloud service provider maintains. Computer system resources are available on-demand, like data storage and computing power, without direct management by the user in Cloud Computing.
Cloud Computing is on-demand to access via the internet from computing resources to applications, servers (physical servers and virtual servers), data storage, development tools, networking capabilities, and more hosted at a remote data center managed by a Cloud Computing Services Provider (CSP). The CSP makes these resources open for a monthly subscription fee or bills them according to usage.
Compared to traditional on-premises, IT companies are relying on the Cloud Computing Services you select; Cloud Computing helps do the following:
The Cloud Platform lets you offload some or most of the costs and effort of purchasing, installing, configuring, and managing your own on-premises infrastructure.
Improve agility and time-to-value:
With Cloud Computing Services, your organization can start using business applications in minutes, instead of waiting for weeks or months for IT to respond to a request, buy and configure supporting hardware, and install software. Cloud Computing Services also lets you empower certain users, specifically developers and data scientists to help themselves with software and support infrastructure.
Scale more efficiently and cost-effectively:
The Cloud Platform provides elasticity. Instead of buying excess capacity that sits unused during slow periods, you can scale capacity up and down in response to spikes and dips in traffic. You can also take advantage of your Cloud Platform provider’s global network to spread your applications closer to users around the world.
The term ‘Cloud Computing’ also refers to the technology that makes the cloud work. This contains some form of virtualized IT infrastructure, servers, operating system software, networking, and other infrastructure that’s abstracted. Using special software, it can be grouped and divided irrespective of physical hardware boundaries. For example, one hardware server can be divided into multiple virtual hardware servers.
Virtualization enables Cloud Platform providers to make maximum use of their data center resources. Many corporations have adopted the Cloud Transformation delivery model for their on-premises infrastructure so they can realize maximum utilization and cost savings over the traditional IT infrastructure and offer the same service to their end-users.
If you use a computer or mobile device at home or at work, you almost certainly use some form of Cloud Computing Services every day.
Instead of storing files on a storage device or hard drive, a user can save them on the Cloud Platform, making it possible to access the files from anywhere, as long as they have access to the web. The Cloud Computing Services hosted on the Cloud Platform can be broadly divided into Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Based on the deployment model, the cloud can also be classified as a public, private, or hybrid cloud.
Further, the Cloud Platform can be divided into two different layers, namely, front-end and back-end. The Cloud Platform layer users interact with is called the front-end layer. This Cloud Computing Architecture enables users to access the data stored in the cloud through Cloud Computing software.
The Cloud Platform layer, made up of software and hardware, i.e., the computers, servers, central servers, and databases, is the back-end layer. This Cloud Computing Architecture layer is the primary component of Cloud Computing services and is entirely responsible for securely storing information. To ensure seamless connectivity between devices linked via cloud platform, the central servers use a software called middleware, (Opens a new window) which acts as a bridge between the database and applications.
Not all clouds are the same, and not every type of Cloud Computing is suitable for everyone. Several different models, types, and services have been developed to help offer the correct solution for your needs. First, you need to choose the type of cloud deployment, or cloud architecture, that your services will be implemented on. There are four different ways to deploy Cloud Computing Services: on a public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, or multi-cloud.
Public clouds are owned and managed by third-party cloud service providers, which provide computing resources like servers and storage over the Internet. Li node, now Akamai, is an example of a public cloud. All hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure is managed by the cloud provider with a public cloud. You can use these services and manage using a web browser, API, or CLI.
Private clouds refer to Cloud Computing resources used exclusively by a single corporation or organization. A private cloud can be physically placed in the company’s onsite data center. Some corporations also pay third-party service providers to host their private cloud service. A private cloud environment supports the services and infrastructure on a private network.
Hybrid clouds deliver a combination of public and private clouds, networked together in such a way that data and applications can be transferred between them. Hybrid clouds give businesses greater flexibility for scaling and deployment.
Multi-clouds is a strategy that techniques two or more cloud computing providers. Multi-clouds strategies offer redundancy and the ability to select different cloud services or features from other providers. Multi-cloud deployments can be valuable in offsetting the cost of testing environments to give internal developers more power at a reduced price.
Most Cloud Computing Services are within these four broad categories: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), serverless, and Software as a Service (SaaS). These are also called the “Cloud Computing Stack” because they are built on top of one another. Knowing what they are and how different they are makes it easier to complete your business goals.
This is the most fundamental category of Cloud Computing services. With IaaS, we can rent IT infrastructure servers and virtual machines, storage, networking, and operating systems from a Cloud Platform provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Cloud Platform as a Service (PaaS) refers to Cloud Computing services that supply an on-demand atmosphere for developing, delivering, testing, and managing software applications. PaaS makes it more comfortable for developers to quickly create web applications or mobile apps without bothering about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure of servers, storage, networking, and databases.
Overlapping with PaaS, Serverless Cloud Computing focuses on making app functionality without spending time on managing the servers and infrastructure needed to do so. The Cloud Computing provider handles the setup, capacity planning, and server management for you. Serverless Cloud Computing architectures are highly scalable and event-driven, only using resources when a specific function or trigger occurs.
Software as a Service is a Cloud Platform method for delivering software applications over the Internet, on-demand, and typically on a subscription basis. With SaaS, Cloud Platform providers host and manage the software (SaaS application) and underlying infrastructure and conduct any maintenance, like software upgrades and security patching. Users link to the application, usually with a web browser on their phone, tablet, or PC over the Internet.
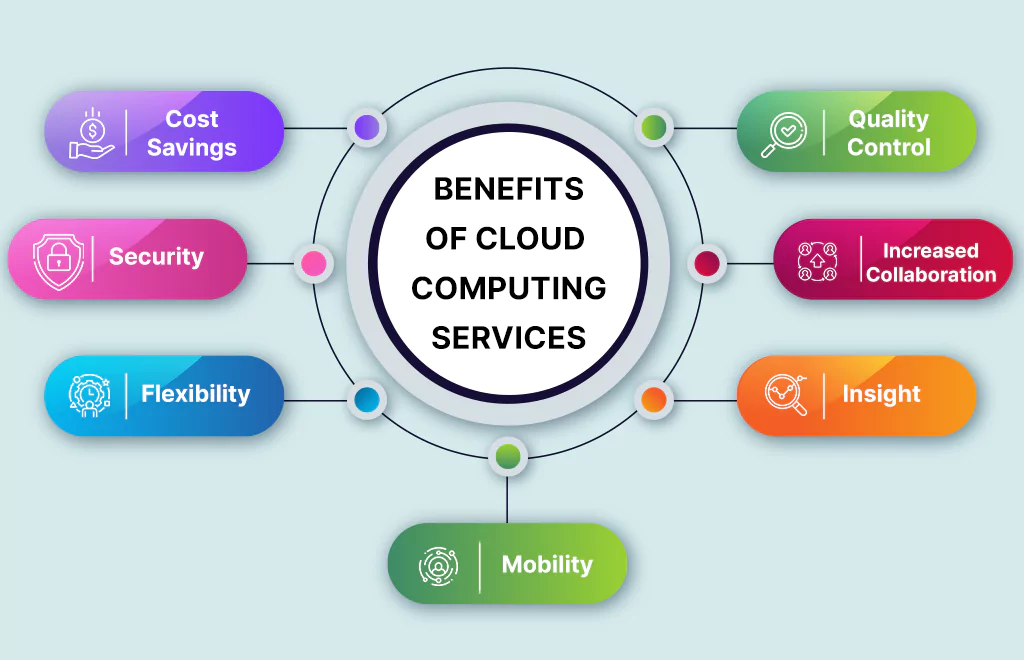
Cloud Platform concerns about the initial cost of cloud adoption are expected, with 20% of organizations expressing apprehension. However, evaluating the Return On Investment (ROI) is crucial. Cloud Computing offers a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to efficiently access data, saving time and money on project startups. This flexible payment approach ensures that businesses only pay for the Types of Cloud Services they use, leading to lower costs. In fact, half of CIOs and IT leaders reported cost savings, due to cloud-based applications.
Security is a top concern for organizations considering Cloud Transformation. The Cloud Platform hosts specialize in monitoring security 24/7, surpassing the efficiency of in-house systems. Cloud Computing Services enhance data protection through encryption during transmission and storage, making it challenging for unauthorized access. Statistics show that 94% of businesses experienced improved security after migrating to the cloud, with 91% finding it more accessible to meet government compliance requirements. Different security settings based on user roles further strengthen data protection.
Dividing attention between various responsibilities can hinder business focus. Cloud Computing provides flexibility by outsourcing IT hosting and infrastructure management. Businesses gain more time to concentrate on core activities, improving efficiency. Cloud Computing Services offer scalability, instantly meeting increased bandwidth demands without complex and costly updates to IT infrastructure. According to an Information Week survey, 65% of respondents consider the ability to quickly meet business demands as a crucial reason for Cloud Transformation.
Cloud Computing Architecture enables mobile access to corporate data through smartphones and devices, accommodating the global use of over 2.6 billion smartphones. This accessibility ensures that employees, especially those with busy schedules or remote locations, can stay updated with clients and coworkers. Cloud Computing Services support convenient information access for travelling sales staff, freelancers, and remote employees, contributing to improved work-life balance. Organizations prioritizing employee satisfaction are up to 24% more likely to expand cloud usage.
Cloud Computing Data holds valuable insights, and cloud-based storage solutions offer integrated analytics for a comprehensive view of organizational data. Storing information on the Cloud Platform makes the implementation of tracking mechanisms and customized reports possible. With actionable insights, businesses can enhance efficiency and develop strategies to meet organizational goals. For example, Sunny Delight increased profits by $2 million annually and reduced staffing costs by $195,000 through Cloud Transformation business insights.
Collaboration is vital for businesses with multiple employees. Cloud Computing Services simplifies collaboration by providing a secure platform for easy sharing of information among team members. Some Cloud Platform-based services even offer collaborative social spaces, fostering employee connection and engagement. While collaboration is possible without Cloud Computing, its ease and effectiveness are unmatched.
Consistency and Quality Control are critical for business success. In a Cloud Platform system, documents are stored in a single format and location, ensuring uniformity and reducing human errors. Centralized storage prevents issues arising from different versions of documents saved in silos, avoiding confusion and maintaining data integrity.
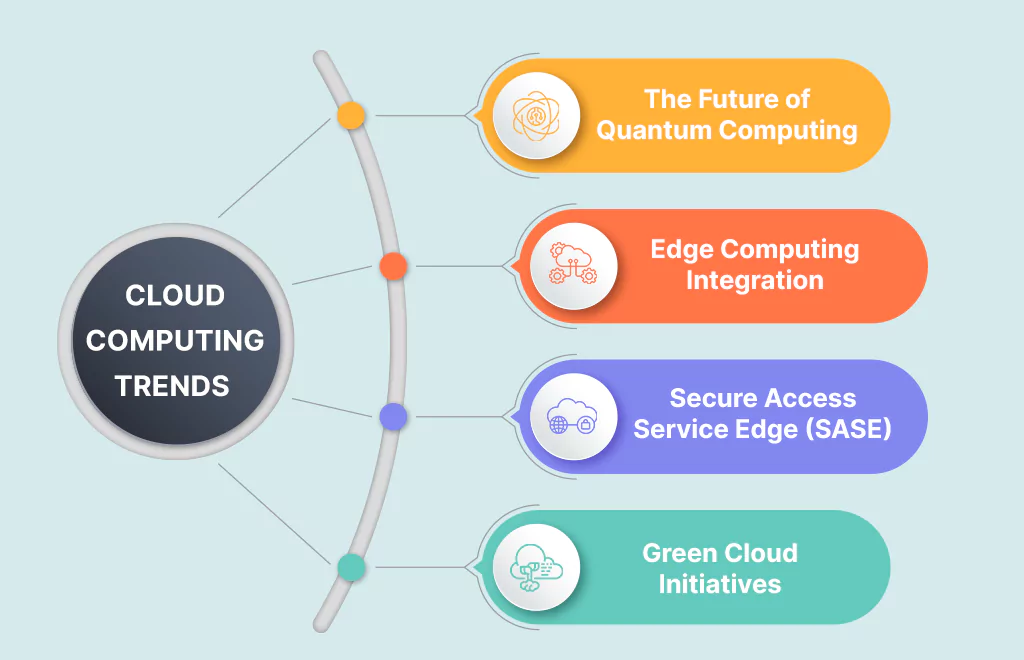
The Future of Quantum Computing:
Cloud Computing is set to harness the power of Quantum Computing, revolutionizing complex calculations and data processing. Quantum computers can handle massive datasets at unprecedented speeds, opening new possibilities for scientific research, cryptography, and advanced simulations.
Edge Computing Integration:
As the Internet of Things (IoT) and latency-sensitive applications grow, cloud providers will increasingly adopt Edge Computing. This involves distributing systems to bring data and processing closer to users, improving efficiency and reducing latency in real-time applications.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE):
Security remains a top concern, and the rise of SASE will play a pivotal role in managing security and risk. This approach combines networking and security functions, providing secure access to cloud-based applications from anywhere in the world.
Green Cloud Initiatives aim to reduce the energy consumption of cloud infrastructure, enhance hardware recycling, minimize electronic waste, aligning cloud services with eco-friendly practices.
Take the Next Step with InfinityHub




 India
India USA
USA


